It's been a while since I did some *real* posting. Time to do one..Sorry, this post is not going to be 100% AX focussed, however towards the end, I will share some thoughts/ideas how AX can leverage if RBS is already part of your infrastructure. I will try to cover RBS Implementation in 2 or 3 posts.
You might be wondering what the heck is RBS? Even I was in the same state, a while ago :). Then, started my journey Implementing SQL RBS (Remote Blob Storage) for Sharepoint 2007/2010 in my current company.
Previously, I had setup and configured RBS successfully with SQL Server 2008 R2, now recently we moved all our servers to cloud and we thought it was the right time to upgrade to SQL Server 2012.
So, I had to do the exercise once more, this time with SQL Server 2012. So, Let me give you a quick introduction to RBS. Towards the end, I will share some few references and links where you can get more details about RBS.
Introduction:
In simple terms, RBS (Remote Blob Storage) is used for externalising your storage to a file system instead of bulking your database thereby providing benefits such as:
a. Optimized database storage
b. Performance
c. Distinction between structured and unstructed data
RBS is designed to move the storage of binary large objects (BLOBs) from database servers to commodity storage solutions
Content-addressable storage, also referred to as associative storage or abbreviated CAS, is a mechanism for storing information that can be retrieved based on its content, not its storage location. It is typically used for high-speed storage and retrieval of fixed content
Scenario
Consider the scenario of a custom application that is designed to provide training content to users. The application will contains less than 1000 documents but they are all training videos that average 200MB in size. The database for this application would be nearly 200GB in size even though there are relatively few documents. By enabling RBS, the binary data for these videos can be kept out of the database while the structured metadata in the database remains responsive and easy to manage
When Storage Tiers Need to be Implemented
One of the most significant benefits of RBS lies in extensibility. RBS doesn’t just have to be for getting BLOB data out of the database. It can serve other creative purposes such as facilitating highly efficient storage tiers.
Scenario
A document management solution has been or will be deployed for an organization. A large percentage of the corporate user base will be adding and editing collaborative content on a daily basis. Over time, a very large number of customer centric documents are created, possibly declared as records for retention, and then archived.
How RBS Helps
In this scenario, an RBS provider that enables a tiered storage platform could provide tremendous cost savings by intelligently managing the storage location of BLOB data.
New and frequently accessed content could be stored in high performance storage.
Older documents that are accessed only occasionally could be automatically moved to lower cost and lower performance storage such as SATA arrays for example.
Then over time, very old documents that are rarely accessed could be automatically moved again to extremely inexpensive cloud based storage.
In all cases, end users are able to access content in real time but the responsiveness and cost of the storage is intelligently managed.
When Storage Needs to be Optimized
When BLOB data is allowed to inflate a SQL database, file I/O and processing load is increased on the database server. If the average size of BLOB data is 80KB or higher, then implementing RBS reduces I/O and processing load which improves the performance of SQL Server
So, Let's jump into some action. I will walkthrough the steps involved for provisioning your blob store.
A. Enable FileStream on the database server
i. Launch SQL Server Configuration Manager (Start > Programs > Microsoft SQL Server 2012 > > Configuration Tools > SQL Server Configuration Manager
ii. Right-click your SQL instance (running MOSS) and then go to Properties, Click FileStream tab

and click the options below Enable filestream for SQL and I/0 Access and allo remote access to filestream data.
Enable file stream settings at database level
B. Provision blob store for each content database in Sharepoint
i. Open SQL Server Management Studio and expand your content database for which you want the blob store to be provisioned for and type in the below queries in sequence:
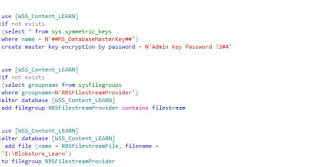
Paste the following SQL queries in Query pane, and then execute them in the sequence listed. In each case, replace [WSS_Content_Learn] with the content database name, and replace I:\BlobStore_Learn with the volume\directory in which you want the BLOB store created. The provisioning process creates a folder in the location that you specify. Be aware that you can provision a BLOB store only one time. If you attempt to provision the same BLOB store multiple times, you will receive an error
Once the queries have been executed, you should be able to see a folder $FSLog and filestream.hdr
C. Install RBS Client Library on the Sharepoint Web Server
Below are the install steps:
Once the installation is completed, then Run the below command with elevated permissions, if required.
Note: This works only for the first time i.e. Setting up RBS for your first content database, To enable RBS on a second content database, there's a separate command which I will discuss later in my post.
msiexec /qn /lvx* rbs_install_log.txt /i "RBS" TRUSTSERVERCERTIFICATE=true FILEGROUP=PRIMARY DBNAME="WSS_Content" DBINSTANCE="DBInstanceName" FILESTREAMFILEGROUP=RBSFilestreamProvider FILESTREAMSTORENAME=FilestreamProvider_1
How to check if the RBS client library installed successfully:
Storage – Installation completed successfully.
2.
On the computer that is running SQL Server 2012, verify that the RBS tables were created in the content database. Several tables should be listed under the content database that have names that are preceded by the letters "mssqlrbs"
Now, to check RBS in action, You can go your sharepoint site, and upload some docs (say which is > 100 k) and you can see binary files getting created in your blob storage, also you can check the folder size and properties of the folder
I will soon come up with Part 2, wherein I will show the steps for enabling a second content database. I had to go through some troubleshooting before I successfully enabled RBS on my second content database.







4 comments:
Great post! This works and easy setup :)
Heya¡my very first comment on your site. ,I have been reading your blog for a while and thought I would completely pop in and drop a friendly note. .
Sharepoint Remote Blob Storage
Great post! Worked like a charm for me.
Here's a txt-version of the sql-commands:
use [WSS_CONTENT]
if not exists
(select * from sys.symmetric_keys
where name = N'##MS_DatabaseMasterKey##')
create master key encryption by password = N'Admin Key Password !2#4'
use [WSS_CONTENT]
if not exists
(select groupname from sysfilegroups
where groupname = N'RBSFilestreamProvider')
alter database [WSS_Content]
add filegroup RBSFilestreamProvider contains filestream
use [WSS_CONTENT]
alter database [WSS_Content]
add file (name = RBSFilestreamFile, filename = 'S:\Blob_Store')
to filegroup RBSFilestreamProvider
Hi There,
thank you for a comprehensive covereage on this article, however there are a couple of steps missing. You need to
1. Enable RBS for each content Datbase
2. Assign db_owner to the web application.
both of these are outlined in the following article
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee748631(v=office.15).aspx
I do apreciate the time saved with your document.
Regards,
Mat
Post a Comment